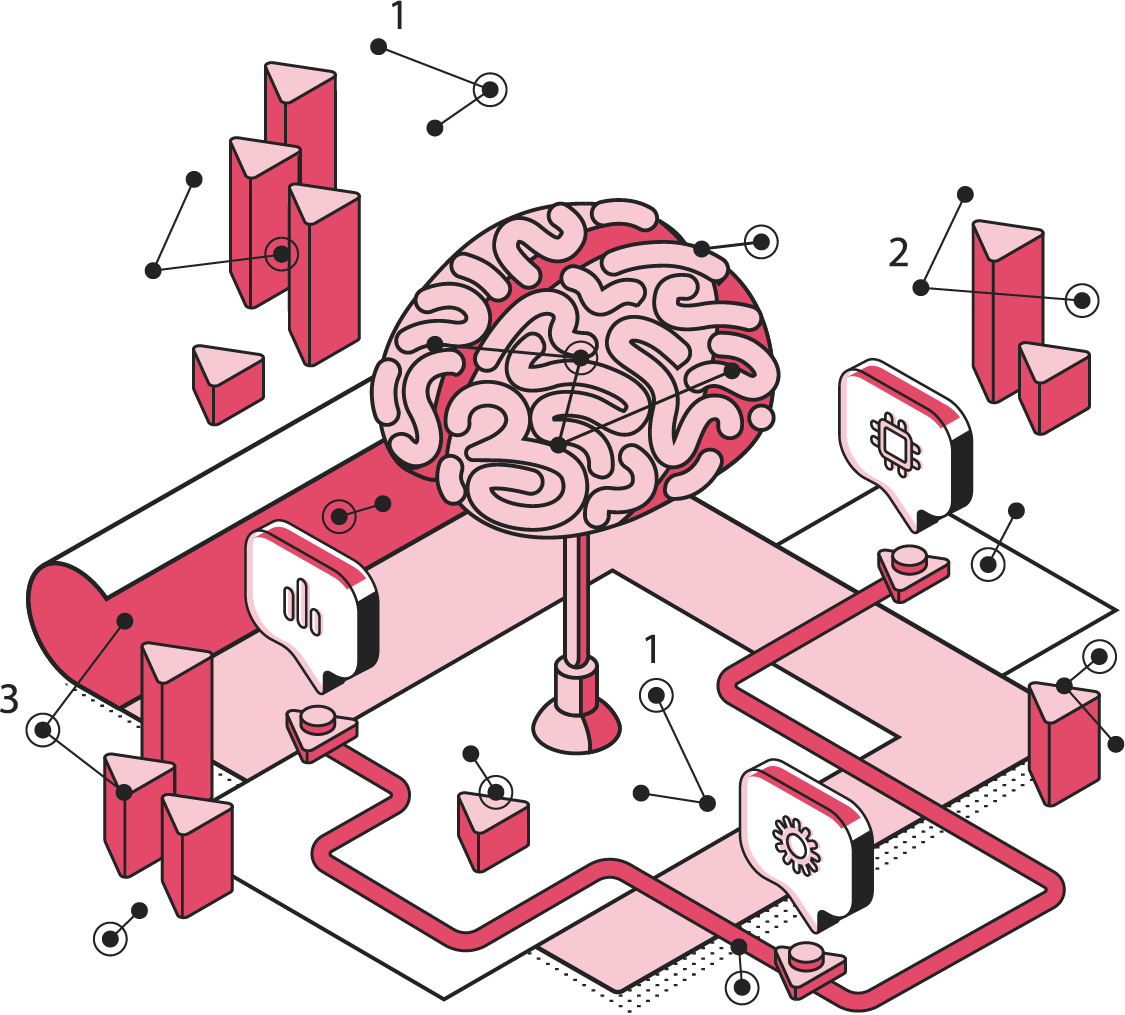
The GLS Legal Operations Centre
Intelligence, resources and execution support
Transformation Tube Map
Knowledge Centre
Legal Dept.
Resources
Managed Legal Services
Members
Resources
Legal Ops
Community
Back
Contracting Line
What Is It
The Contracting Function governs how commercial intent is converted into enforceable legal obligations.
Within a modern legal department, it is not a drafting service or a reactive review function. It is a strategic operating capability that determines deal velocity, risk allocation, value protection, and downstream dispute exposure.
An effective contracting function expresses the organisation’s risk appetite, commercial priorities, and governance standards through structured, repeatable contracting practices.
When designed properly, it enables the business to contract at speed without sacrificing control.
Contracting is therefore not a series of isolated transactions. It is an industrial system that must operate consistently across volume, geographies, counterparties, and transaction types.
Modern legal teams must now have a constant focus on driving performance improvements across the full contract lifecycle, governed by the organisation’s Group Legal Policy, in a way that delivers maximum value back to the Business.
The GLS Contracting Line shows you how it is done.
Business Importance
The Contracting Function is business-critical because it establishes the legal, commercial, and governance foundations on which contractual relationships depend.
Without disciplined contracting, organisations are exposed to inconsistent risk allocation, unclear authority, and avoidable disputes.
In practice, contracting determines:
◼️ Deal Generation & Conversion: turns pipeline opportunities into signed, enforceable deals with predictable closure timelines.
◼️ Revenue Capture & Cash Assurance: embeds pricing, invoicing triggers, acceptance criteria, and payment terms to accelerate cash and reduce disputes.
◼️ Risk Allocation Discipline: sets balanced, policy‑aligned positions (liability caps, indemnities, warranties, IP rights, compliance) to contain exposure supported by formal risk sign-off thresholds.
◼️ Operational Certainty: locks in delivery conditions (SLAs, KPIs, remedies) for post‑award performance and escalation paths.
◼️ Supply Chain Stability: ensures availability, continuity, and resilience via termination rights, step‑in, dual sourcing, and force majeure handling.
◼️ Compliance Embedding: bakes in data protection, sanctions/export, ABC/AML, ESG, H&S to avoid regulatory friction.
◼️ Market Entry Enablement: de‑risks new geographies/products via localised templates and jurisdictional playbooks.
◼️ Decision Governance: clarifies approval workflows, risk sign‑offs, and DoA to prevent defective authorisations.
◼️ Stakeholder Experience: creates a predictable, fair‑dealing posture that counterparties trust and prefer.
◼️ Data & Insight: provides contract‑level analytics (cycle times, deviations, margin leakage) to steer improvements.
◼️ Scalability: standardisation and automation allow the Business to scale deal volume without degrading quality.
These factors explain why a structured contracting function is a non-negotiable feature of any organisation operating at scale.
Business Value
Once these foundations are in place, the Contracting Function becomes a source of measurable business value, influencing speed, predictability, cost control, and long-term commercial performance. The “value” to the Business includes:
◼️ Time-to-Close Compression: faster negotiation and approvals through standard templates, playbooks, and SLAs-directly impacting quarterly revenue recognition.
◼️ Margin Protection: policy‑aligned clauses (indexation, caps, price adjustment, limits of liability) reduce value dilution and defend pricing power.
◼️ Value Seepage Prevention: stronger post‑award governance (KPIs, remedies, change control) curbs scope creep, write‑offs, and leakage.
◼️ Dispute Avoidance & Cost Reduction: clearer obligations and evidence reduce disputes, external counsel spend, and management distraction.
◼️ Cash Acceleration: unambiguous acceptance milestones and payment terms increase DSO discipline and forecasting accuracy.
◼️ Operational Predictability: repeatable outcomes and clean escalations lower disruption risk and increase delivery certainty.
◼️ Better Negotiation Outcomes: RPLV framing and deviation controls improve leverage, speed, and settlement quality.
◼️ Portfolio Insight: analytics expose bottlenecks, risky deviations, supplier/counterparty trends-enabling prune/maintain/grow decisions.
◼️ Scalable Throughput: automation and tiered reviews handle higher volumes at lower marginal cost, without sacrificing control.
◼️ Reputation & Trust: consistent, reasonable positions enhance market reputation; preferred‑partner status wins more deals.
This value is only realised when contracting is treated as a system, not a collection of documents.
Best Practice Features
The best practice features of an optimised Contracting Function include:
◼️ Data-Led Current State Assessment: a fact-based view of contracting performance, including volumes, cycle times, deviation rates, dispute correlation, and legal effort allocation, supported by ongoing analytics.
◼️ Offline Process Optimisation (Before Technology): contracting processes are designed and stabilised offline, with clear definitions of contract types, risk tiers, review protocols, approval thresholds, and supporting templates.
◼️ Disciplined Tech Enablement (After Foundations Are Fixed): technology is introduced only once processes are clear and repeatable, ensuring systems amplify discipline and align with the chosen CLMS.
◼️ Contracting Policy (GLP Aligned): expresses a range of permissible outcomes (preferred / acceptable / exceptional) for key risk positions and commercial terms.
◼️ Template Library & Clause Bank: harmonised templates with jurisdictional variants, standard clauses with approved fallbacks, and redline guidance.
◼️ SMART Schedules: pre‑built commercial schedules for scope, KPIs, pricing, milestones, acceptance, change control, and termination-plug‑and‑play.
◼️ Negotiation Playbooks & Checklists: Playbooks are the control layer of the contracting function - they offer point‑by‑point tactics, concession ladders, and deal hygiene checklists to keep negotiations disciplined.
◼️ Tiered Review Protocols: risk‑based routing (self‑service, paralegal, counsel, specialist) with clear SLAs to avoid over‑lawyering.
◼️ Approval Workflow & Risk Sign‑Off: DoA matrices; mandatory risk sign‑offs for exceptions; escalation paths for out‑of‑policy positions.
◼️ Performance‑Based Contracting: measurable KPIs, credits, remedies, and continuous improvement provisions to protect post‑award value.
◼️ Contract Administration: post‑signature obligations tracking, variations/change orders, notice management, and obligation calendars.
◼️ Quality Assurance & Auditing: sample reviews, deviation analytics, and lessons‑learned loops informed by disputes/claims data.
◼️ Deal Memory: capture of negotiation rationale and exceptions for future leverage and portfolio learning.
◼️ Authorized Signatories & E‑Signature: robust signatory control and secure e‑signature workflows to prevent defective execution.
◼️ Policy Library Integration: privacy, sanctions/export, ABC/AML, information security, IP-embedded cross‑references.
◼️ Contract Analytics: dashboards for cycle time, deviation frequency, margin impact, dispute trends, supplier performance.
◼️ Value Seepage Recovery & Dispute Detection: triggers, alerts, and early intervention protocols; preventive playbooks.
◼️ Self‑Help Resources: FAQ, quick guides, training modules for front‑line users to reduce low‑value legal requests.
◼️ Legal Tech Contracting Tools: CLMS, document automation, intake/workflow, clause recommendation, e‑billing integration.
◼️ Records & DMS Discipline: authoritative repositories, version control, metadata, retention schedules, audit trails.

GLS Contracting Doctrine
The Contracting Line operates through a set of critical resource enablers, referred to as Stations on the GLS Legal Dept. Transformation Tube Map. Each Station addresses a specific control point in the contracting lifecycle. Individually, they strengthen execution.
To make better sense of your Contracting Function, we have developed what we call the GLS Contracting Doctrine to help you apply a coherent operating architecture that replaces ad-hoc, artisanal contracting with an industrial, repeatable model that unleash substantial value to the Business.
You can review the GLS Contracting Doctrine - How to Engineer an Industrial Scale Contracting Function in full but below we set out the conceptual spectrum of which optimally performing contracting function operates together with its major anatomical parts.
Governance & Authorisation
◼️ Legal Department Service Charter
◼️ Authorised Signatories & Delegation Protocols
Contract Intake & Prioritisation
◼️ Legal Services Request Form
Operational Execution
◼️ Clause Bank & Playbooks
◼️ Document Authoring & Execution Tools
◼️ Review Protocols & Checklists
Risk and Value Capture
◼️ Risk Sign-Off & Value Seepage Recovery
◼️ SMART Schedules & Contracting Analytics
Ongoing Management & Compliance
◼️ Contract Performance & Administration
◼️ Quality Assurance & Auditing
Technology Enablement
Productivity Consequences
A poorly optimised contracting function will give rise to:
◼️ Excessive Closure Times: unclear templates and ad‑hoc workflows extend time‑to‑signature and miss revenue windows.
◼️ Inflated Legal Costs: the internal/external cost of supporting the contracting process inflates.
◼️ Inconsistent Risk Profile: unmanaged deviations create portfolio volatility and weaken negotiation posture.
◼️ Revenue Leakage: weak schedules and post‑award governance cause scope creep, credit exposure, and write‑offs.
◼️ Dispute Incidence: ambiguity and poor evidence discipline drive claims, escalations, and legal spend.
◼️ Defective Authorisations: broken DoA/signatory controls result in invalid agreements and remediation costs.
◼️ Rework & Bottlenecks: non‑standard drafting and over‑lawyering clog pipelines; stakeholder frustration rises.
◼️ Poor Tech Adoption: CLMS and automation fail when offline processes, data, and policy discipline are weak.
◼️ Audit Pain: missing deal memory and weak records create long, costly audits and diligence delays.
◼️ Brand & Counterparty Friction: unpredictable positions damage reputation; preferred partner status evaporates.
◼️ Legal Value Undercut: activity‑only metrics obscure outcomes; perceptions of legal effectiveness decline.
Tech Implications
Technology does not fix contracting. It amplifies whatever discipline already exists.
A key Golden Rule to help you safeguard against this risk is – if it doesn’t work offline, then it wont work online.
When foundations are sound, technology enables:
◼️ CLMS: electronic platform for generation, negotiation, approval, obligation tracking, and archiving; integrates with playbooks, clause banks, and workflows.
◼️ Document Automation: rapid assembly of templates and schedules; data‑field governance to minimise drafting errors.
◼️ AI Contract Reviews: issue spotting, deviation detection, fallback suggestions; emerging auto‑redlining remains nascent-use within policy controls.
◼️ Workflow & Intake Automation: request classification, routing, SLAs, and escalation visibility; links to risk sign‑offs and DoA.
◼️ E‑Signature & Identity: secure execution with audit trails; signatory validation and seal/affix requirements where applicable.
◼️ Analytics & Dashboards: cycle‑time, deviation rates, margin impact, dispute trends, value seepage indicators-management‑grade.
◼️ DMS Integration: authoritative repository, retention schedules, metadata, and search-supporting audits and discovery.
◼️ Golden Rule: If the contracting function doesn’t work offline (policy, templates, playbooks, workflows), it won’t work online. Tech magnifies discipline; it doesn’t create it.
What Next?
Each Station on the Contracting Line can be explored in detail to understand how it operates, what good looks like, and how it integrates with the broader legal operating model.
We have given you a visual recommendation of what a world-class contracting function might look like – allowing you to access the power of comparison as you start your transformation work.
We are not saying that your contracting function must look precisely as we have modelled, what works for you is what works for you in your operating context. However, you can now plan for that with greater certainty and efficiency by examining world class North Star markers.
Together, these Stations provide a practical blueprint for building a contracting function that is fast, controlled, scalable, and trusted by the business.
Contract Function: Final Thoughts
Contracting is one of the few legal functions where small design choices compound quickly — for better or worse.
Treat it as an artisanal craft where outcomes depend on individuals – however, it should be designed as an industrial system such that outcomes become predictable, defensible, and scalable.
As you plan your legal dept. transformation, the contracting function will take centre stage because it’s more mature, more visible to internal clients, and tethered directly to revenue.
There are loads of easy interventions that deliver back time and money to the Business – not to mention an enhanced capability for the Business “to get business done”. Wins here count - and they count loudly.
It is safe ground to operate on – and the footprints of success are clearly laid out in the sand to follow. Big gains, low risk. No excuses.
That is the purpose of the GLS Contracting Line.

The GLS Legal Operations Centre
Register to access your complimentary Day 1 Resource Stack packed with legal team performance resources.
GLS Ultimate Guide To Legal Operations
Download this and read it thoroughly and regularly. It is a wonderful transformation companion.

Book A No-Obligation Consultation
If you would like discuss your legal transformation needs, please book a 30 minute free consultation with us.

GLS Legal Transformation Boot Camp
Our hugely successful, 10-week long, email-based boot camp on how to effectively transform your legal team.